Blog
- What impurities can edible oil refining equipment remove during processing?
- Ultimate guide to palm kernel oil processing machines: types & how they work
- What is the working principle of crude palm kernel oil expeller?
- Batch type edible oil refining machine 1tpd to 20tpd
- Must-know maintenance tips for your soybean oil extraction machine
Contact Us
- Mobile/WhatsApp:
008613526627860
- Phone:
008637156771823
- Email:
sales@doingoilmachine.com
News
- 2tph Drum-type Palm Fruit Threshing Machine: New Order Secured by Henan Doing Nig. Co.,Ltd from Nigeria
- Shipping Confirmation: Mini Palm Oil Processing Line Successfully Handed Over from Our Nigeria Branch
- Heading to Kenya! Henan Glory's Custom Sunflower Oil Extraction Equipment Is On the Move
- Shipment Update: Small Scale Palm Oil Mill Plants Successfully Shipped to Nigeria
- Tailored for 1TPD: Henan Glory Wins Nigerian Small Scale Palm Oil Production Equipment Order
What impurities can edible oil refining equipment remove during processing?
High-quality edible oil starts with effective refining. Crude vegetable oils contain various impurities that affect safety, taste, appearance, and shelf life. Professional edible oil refining equipment is designed to systematically remove these unwanted components, transforming crude oil into clear, stable, and market-ready products. This process is crucial for meeting both consumer expectations and strict food safety standards. In this article, we’ll explore the key impurities removed during refining and how advanced engineering ensures optimal results.
1. Solid Impurities & Suspended Particles
Sources: Seed fragments, dirt, sand, and other fine materials from harvesting, transportation, and initial mechanical pressing or extraction.
Removal Method: Initial screening, filtration, sedimentation, or centrifugation.
Why It Matters: Removing these solids protects edible oil refining equipment from wear and clogging and is the essential first step toward a visually clean edible oil.
 Edible oil filtration equipment
Edible oil filtration equipment
2. Phospholipids (Gums)
Sources: Naturally present in seeds like soybeans and canola.
Removal Method: Degumming with water (for hydratable gums) or acids/enzymes (for non-hydratable gums bound to minerals).
Why It Matters: If not removed, gums can cause darkening, off-flavors, haze in bottled oil, and excessive foaming or sediment formation during frying. It's worth mentioning that Henan Glory Company's advanced edible oil refining equipment utilizes highly efficient hydration or acid degumming processes to ensure the complete removal of gums.
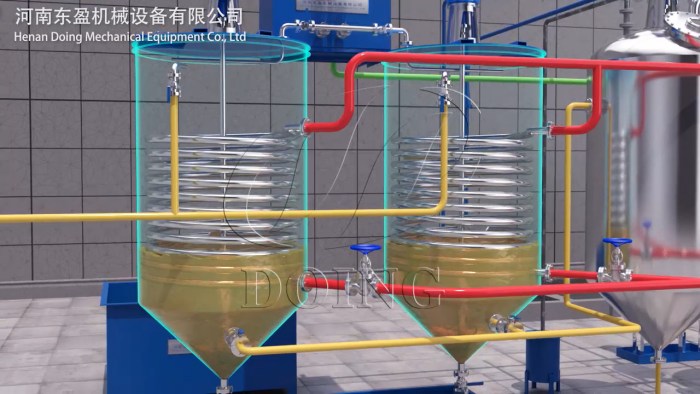 Edible oil degumming equipment
Edible oil degumming equipment
3. Free Fatty Acids (FFA)
Sources: Result from the breakdown of triglycerides during storage or processing of oilseeds.
Removal Method: Neutralization (Chemical Refining) with an alkali to form soapstock, or Distillation (Physical Refining) using steam under high temperature and vacuum.
Why It Matters: FFAs directly contribute to rancidity, unpleasant taste and odor, and significantly lower the oil's smoke point, making it unsuitable for high-temperature cooking.
4. Coloring Pigments
Sources: Natural pigments such as chlorophyll (green) and carotenoids (red/yellow, e.g., beta-carotene).
Removal Method: Adsorption using adsorbent materials like activated clay or bleaching earth.
Why It Matters: It can improve the appearance and stability of edible oils, resulting in clear, light-colored cooking oil. Some pigments also act as photosensitizers, accelerating oil oxidation and spoilage. Modern edible oil decolorization equipment is designed for maximum pigment and impurity adsorption with minimal oil loss.
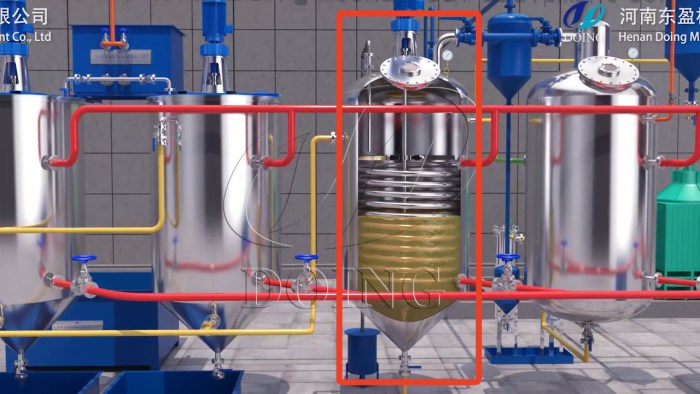 Edible oil decolorization equipment
Edible oil decolorization equipment
5. Off-Flavors and Odors
Sources: A complex mix of volatile organic compounds from oxidation or inherent to the crude oil.
Removal Method: Deodorization, a high-temperature, high-vacuum steam distillation process.
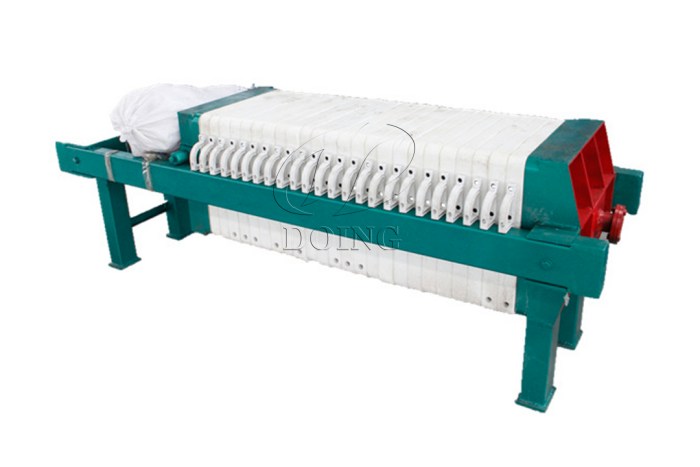
Why It Matters: This critical step creates a neutral, bland-flavored oil, which is the standard for most cooking and food manufacturing applications. Henan Glory's edible oil deodorization equipment or deodorization tower is optimized for efficient stripping of volatiles while preserving the oil's nutritional quality.
 Edible oil deodorization tower
Edible oil deodorization tower
6. Waxes and Sterols
Sources: Waxes are present in oils like sunflower, rice bran, and corn oil. Sterols are natural minor components.
Removal Method: Winterization/Dewaxing—cooling the oil to crystallize waxes, followed by filtration.
Why It Matters: Waxes cause unsightly cloudiness and sedimentation when oil is stored at cool temperatures, a major quality concern for retail bottles.
7. Oxidation Products
Sources: Primary (peroxides) and secondary (aldehydes, ketones) products formed when oil is exposed to air, light, or heat.
Removal Method: Bleaching clay adsorbs many secondary products, while deodorization strips away volatile compounds responsible for rancid smells.
Why It Matters: Removing these products is essential for improving the oil's sensory quality and extending its shelf life.
8. Trace Metals
Sources: Iron, copper, lead, etc., from soil, processing equipment, or catalysts.
Removal Method: Chelation during acid degumming and adsorption during bleaching.
Why It Matters: Iron and copper are powerful pro-oxidants that drastically reduce oil stability and promote rancidity.
 Soil
Soil
9. Pesticide Residues & Environmental Contaminants
Sources: Agricultural chemicals or pollutants from contaminated soil or smoke-drying.
Removal Method: Adsorption using activated carbon added during bleaching, and volatilization during high-temperature deodorization.
Why It Matters: This is a critical food safety function, ensuring that the final product meets food safety standards.
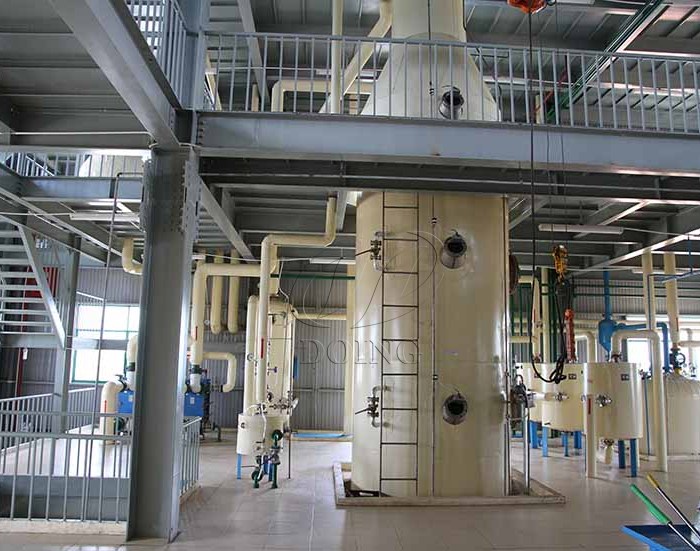
10. Mycotoxins
Sources: Toxins like aflatoxin from mold-contaminated seeds (e.g., peanuts, corn).
Removal Method: A combination of alkali refining and adsorption with activated bleaching earth or carbon is highly effective.
Why It Matters: Another vital food safety measure to eliminate these potent biological hazards.
 Mold-contaminated corns
Mold-contaminated corns
Edible oil refining equipment is engineered to systematically remove diverse impurities—from those affecting appearance and performance to those posing serious health risks. The ultimate goal is to produce a consistent, high-quality, and safe product that meets both consumer expectations and rigorous international food standards, while preserving the oil's nutritional value as much as possible. If you would like to learn more about edible oil refining equipment, contact Henan Glory today for expert consultation on designing or optimizing your edible oil refining equipment.
Leave a message
If you wanna to get more details about What impurities can edible oil refining equipment remove during processing?, you can send E-mail to sales@doingoilmachine.com. Or you can consult our professional engineers and specialized sales team by leaving a message in below form. We will contact you ASAP. You also can visit our factory in Henan, China.